noun Physiology.
- the change in electrical potential that occurs between the inside and outside of a nerve or muscle fiber when it is stimulated, serving to transmit nerve signals.
noun
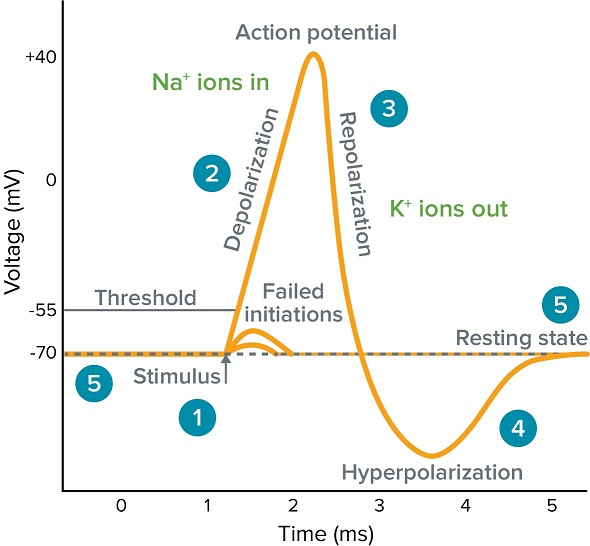
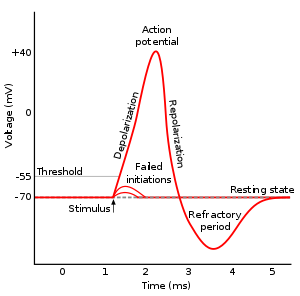
- a localized change in electrical potential, from about –70 mV to +30 mV and back again, that occurs across a nerve fibre during transmission of a nerve impulse
n.
- The change in membrane potential occurring in nerve, muscle, or other excitable tissue when excitation occurs.
- A momentary change in electrical potential on the surface of a neuron or muscle cell. Nerve impulses are action potentials. They either stimulate a change in polarity in another neuron or cause a muscle cell to contract.
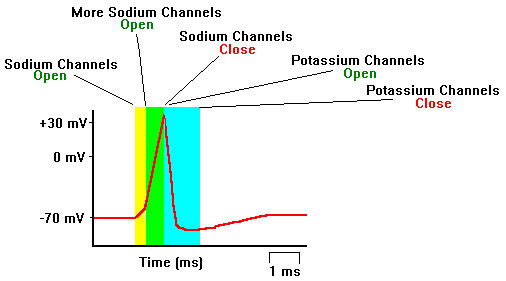
The rapid change in electric potential that parts of a nerve cell undergo when a nerve impulse is generated. Unlike ordinary electric current (see also current), which consists of the flow of electrons, the action potential involves the movement of sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary