noun
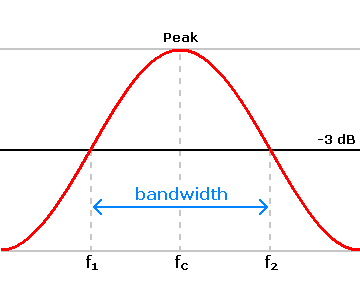
- Telecommunications. the smallest range of frequencies constituting a band within which a particular signal can be transmitted without distortion.
- Digital Technology. the transmission capacity of an electronic communications device or system; the speed of data transfer: a high-bandwidth Internet connection.
- mental capacity; intelligence: Don’t listen to him—he has really low bandwidth.
- a person’s capacity to handle or think about more than one thing at the same time: He doesn’t have the bandwidth to make those kinds of decisions.
noun
- the range of frequencies within a given waveband used for a particular transmission
- the range of frequencies over which a receiver or amplifier should not differ by more than a specified amount
- the range of frequencies used in a specific telecommunications signal
- The numerical difference between the upper and lower frequencies of a band of electromagnetic radiation, especially an assigned range of radio frequencies.
- The amount of data that can be passed along a communications channel in a given period of time. For analog devices, such as standard telephones, bandwith is the range of frequencies that can be transmitted and is expressed in hertz (cycles per second). For digital devices, bandwidth is measured in bits per second. The wider the bandwidth, the faster data can be sent.
The amount of data that can be carried by a digital communication medium, often expressed in hertz.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary