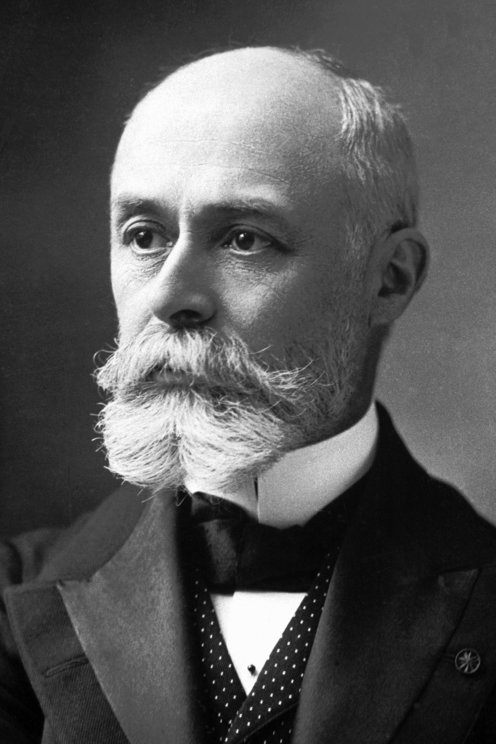< /ɑ̃ˈtwan ɑ̃ˈri/, 1852–1908, French physicist (son of Alexandre Edmond): Nobel Prize 1903.
noun
- the derived SI unit of radioactivity equal to one disintegration per secondSymbol: Bq
noun
- Antoine Henri (ɑ̃twan ɑ̃ri). 1852–1908, French physicist, who discovered the photographic action of the rays emitted by uranium salts and so instigated the study of radioactivity: Nobel prize for physics 1903
n.
- A unit of measurement of radioactivity, equal to one disintegration per second.
- The SI derived unit used to measure the rate of radioactive decay. When the nucleus of an atom emits nucleons (protons and/or neutrons) and is thereby transformed into a different nucleus, decay has occurred. A decay rate of one becquerel for a given quantity means there is one such atomic transformation per second.
- Family of French physicists, including Antoine César (1788-1878), one of the founders of the science of electrochemistry; his son Alexandre Edmond (1820-1891), noted for his research on phosphorescence, magnetism, electricity, and optics; and his grandson Antoine Henri (1852-1908), who discovered spontaneous radioactivity in uranium. Antoine Henri Becquerel’s work led to the discovery of radium by Marie and Pierre Curie, with whom he shared the 1903 Nobel Prize for physics.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary