cholesterol [kuh-les-tuh-rohl, -rawl] ExamplesWord Origin noun Biochemistry.
- a sterol, C27H46O, that occurs in all animal tissues, especially in the brain, spinal cord, and adipose tissue, functioning chiefly as a protective agent in the skin and myelin sheaths of nerve cells, a detoxifier in the bloodstream, and as a precursor of many steroids: deposits of cholesterol form in certain pathological conditions, as gallstones and atherosclerotic plaques.
- the commercial form of this compound, obtained from the spinal cord of cattle, used chiefly as an emulsifying agent in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, and in the synthesis of vitamin D.
Also cho·les·ter·in [kuh-les-ter-in] /kəˈlɛs tər ɪn/. Origin of cholesterol 1890–95; chole- + Greek ster(eós) solid + -ol1 Examples from the Web for cholesterin Historical Examples of cholesterin
The fces of animals that live on vegetables contain neither excretin, butyric acid, nor cholesterin.
Arnold Cooley
Such are the constituents, according to Harley, of the usual concretion, the cholesterin calculus.
A System of Practical Medicine By American Authors, Vol. II
Various
The mucus is the colloid; cholesterin, lime, and soda salts are the crystalloids.
A System of Practical Medicine By American Authors, Vol. II
Various
Besides other agencies due to advancing life, the increase of cholesterin is an influential factor.
A System of Practical Medicine By American Authors, Vol. II
Various
The liver also takes out from the blood a waste substance which has the formidable name of cholesterin.
Ernest G. Martin
British Dictionary definitions for cholesterin cholesterol noun
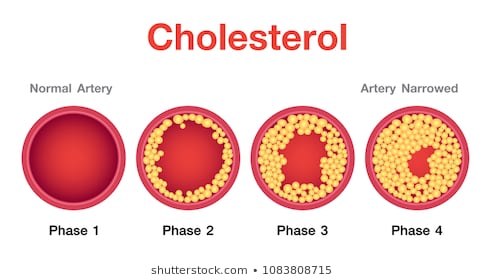
- a sterol found in all animal tissues, blood, bile, and animal fats: a precursor of other body steroids. A high level of cholesterol in the blood is implicated in some cases of atherosclerosis, leading to heart disease. Formula: C 27 H 45 OHFormer name: cholesterin (kəˈlɛstərɪn)
Word Origin for cholesterol C19: from chole- + Greek stereos hard, solid, so called because first observed in gallstones Word Origin and History for cholesterin cholesterol n.
white, solid substance present in body tissues, 1894, earlier cholesterin, from French cholestrine (Chevreul, 1827), from Greek khole “bile” (see cholera) + steros “solid, stiff” (see sterility). So called because originally found in gallstones (Conradi, 1775). The name was changed to the modern form (with chemical suffix -ol, denoting an alcohol) after the compound was discovered to be a secondary alcohol.
cholesterin in Medicine cholesterin [kə-lĕs′tər-ĭn] n.
- Cholesterol.
cholesterol [kə-lĕs′tə-rôl′, -rōl′] n.
- A white crystalline substance found in animal tissues and various foods, normally synthesized by the liver and important as a constituent of cell membranes and a precursor to steroid hormones. Its level in the bloodstream can influence the pathogenesis of certain conditions, such as the development of atherosclerotic plaque and coronary artery disease.
cholesterin in Science cholesterol [kə-lĕs′tə-rôl′]
- A sterol found widely in animal and plant tissues. It is a main component of blood plasma and cell membranes, and it is an important precursor of many steroid hormones (such as the estrogens, testosterone, and cortisol), vitamin D2, and bile acids. In vertebrates, cholesterol is manufactured by the liver or absorbed from food in the intestine. Higher than normal amounts of cholesterol in the blood are associated with higher risk for developing coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis. Chemical formula: C27H46O. See also high-density lipoprotein low-density lipoprotein.
cholesterin in Culture cholesterol [(kuh-les-tuh-rawl, kuh-les-tuh-rohl)]
A white soapy substance found in the tissues of the body and in certain foods, such as animal fats, oils, and egg yolks. Cholesterol has been linked to heart disease and atherosclerosis. (It collects on the walls of arteries and interferes with the flow of blood.) High levels of cholesterol in the blood are considered to be unhealthy. (See saturated fats, HDL, and LDL.)
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary