chronic glaucoma noun Ophthalmology.
- See under glaucoma.
glaucoma [glaw-koh-muh, glou-] noun
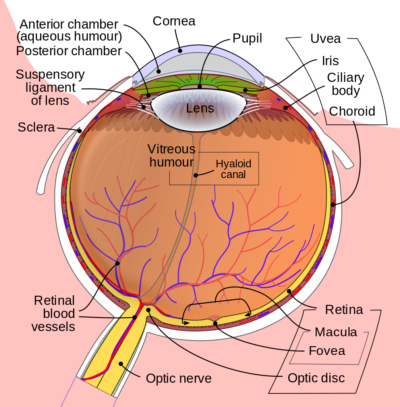
- Ophthalmology. abnormally high fluid pressure in the eye, most commonly caused either by blockage of the channel through which aqueous humor drains (open-angle glaucoma or chronic glaucoma) or by pressure of the iris against the lens, which traps the aqueous humor (angle-closure glaucoma or acute glaucoma).
Origin of glaucoma First recorded in 1635–45, glaucoma is from the Greek word glaúkōma opacity of the eye lens. See glauco-, -oma Related formsglau·co·ma·tous [glaw-koh-muh-tuh s, -kom-uh-, glou-] /glɔˈkoʊ mə təs, -ˈkɒm ə-, glaʊ-/, adjective British Dictionary definitions for chronic glaucoma glaucoma noun
- a disease of the eye in which pressure within the eyeball damages the optic disc, impairing vision, sometimes progressing to blindness
Derived Formsglaucomatous, adjectiveWord Origin for glaucoma C17: from Latin, from Greek glaukōma, from glaukos; see glaucous Word Origin and History for chronic glaucoma glaucoma n.
1640s, from Greek glaukoma “cataract, opacity of the lens” (cataracts and glaucoma not distinguished until c.1705), from -oma + glaukos, an adjective of uncertain origin (see glaucous).
chronic glaucoma in Medicine glaucoma [glou-kō′mə, glô-] n.
- Any of a group of eye diseases characterized by abnormally high intraocular fluid pressure, damaged optic disk, hardening of the eyeball, and partial to complete loss of vision.
Related formsglau•co′ma•tous (-kō′mə-təs) adj. chronic glaucoma in Science glaucoma [glou-kō′mə, glô-]
- A disease of the eye in which the pressure of fluid inside the eyeball is abnormally high, caused by obstructed outflow of the fluid. The increased pressure can damage the optic nerve and lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
chronic glaucoma in Culture glaucoma [(glow-koh-muh, glaw-koh-muh)]
A disease of the eye marked by increased fluid pressure in the eyeball. Glaucoma can damage the optic nerve and may result in blindness if not treated. Surgery may be required for severe cases.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary