noun
- (often initial capital letter) the planet third in order from the sun, having an equatorial diameter of 7926 miles (12,755 km) and a polar diameter of 7900 miles (12,714 km), a mean distance from the sun of 92.9 million miles (149.6 million km), and a period of revolution of 365.26 days, and having one satellite.
- the inhabitants of this planet, especially the human inhabitants: The whole earth rejoiced.
- this planet as the habitation of humans, often in contrast to heaven and hell: to create a hell on earth.
- the surface of this planet: to fall to earth.
- the solid matter of this planet; dry land; ground.
- soil and dirt, as distinguished from rock and sand; the softer part of the land.
- the hole of a burrowing animal; lair.
- Chemistry. any of several metallic oxides that are difficult to reduce, as alumina, zirconia, and yttria.Compare alkaline earth, rare earth.
- Also called earth color. Fine Arts. any of various pigments consisting chiefly of iron oxides and tending toward brown in hue.
- Chiefly British Electronics. a ground.
- Archaic. a land or country.
verb (used with object)
- Chiefly British Electronics. to ground.
- move heaven and earth. heaven(def 8).
- on earth, in the world: Where on earth have you been?
- run to earth,
- Hunting.to chase (an animal) into its hole or burrow: to run a fox to earth.
- to search out; track down: They ran the fugitive to earth in Algiers.
noun
- (sometimes capital) the third planet from the sun, the only planet on which life is known to exist. It is not quite spherical, being flattened at the poles, and consists of three geological zones, the core, mantle, and thin outer crust. The surface, covered with large areas of water, is enveloped by an atmosphere principally of nitrogen (78 per cent), oxygen (21 per cent), and some water vapour. The age is estimated at over four thousand million years. Distance from sun: 149.6 million km; equatorial diameter: 12 756 km; mass: 5.976 × 10 24 kg; sidereal period of axial rotation: 23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds; sidereal period of revolution about sun: 365.256 daysRelated adjectives: terrestrial, tellurian, telluric, terrene
- the inhabitants of this planetthe whole earth rejoiced
- the dry surface of this planet as distinguished from sea or sky; land; ground
- the loose soft material that makes up a large part of the surface of the ground and consists of disintegrated rock particles, mould, clay, etc; soil
- worldly or temporal matters as opposed to the concerns of the spirit
- the hole in which some species of burrowing animals, esp foxes, live
- chem See rare earth, alkaline earth
-
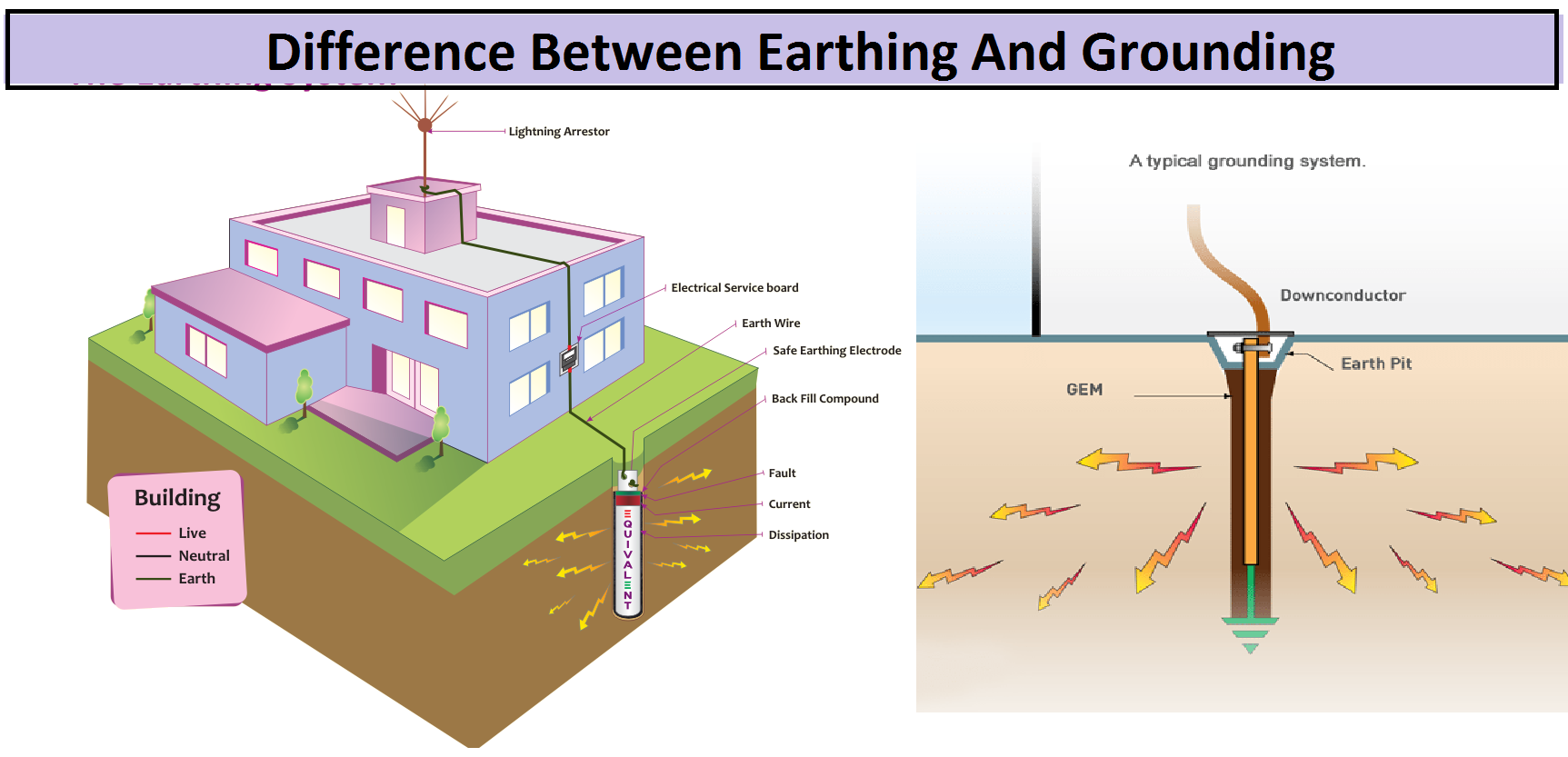
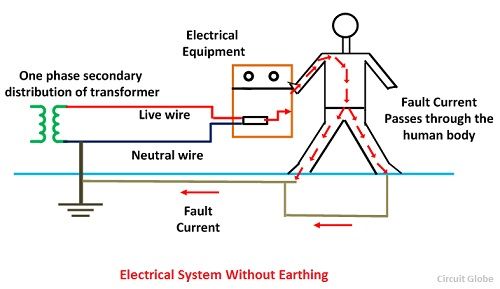
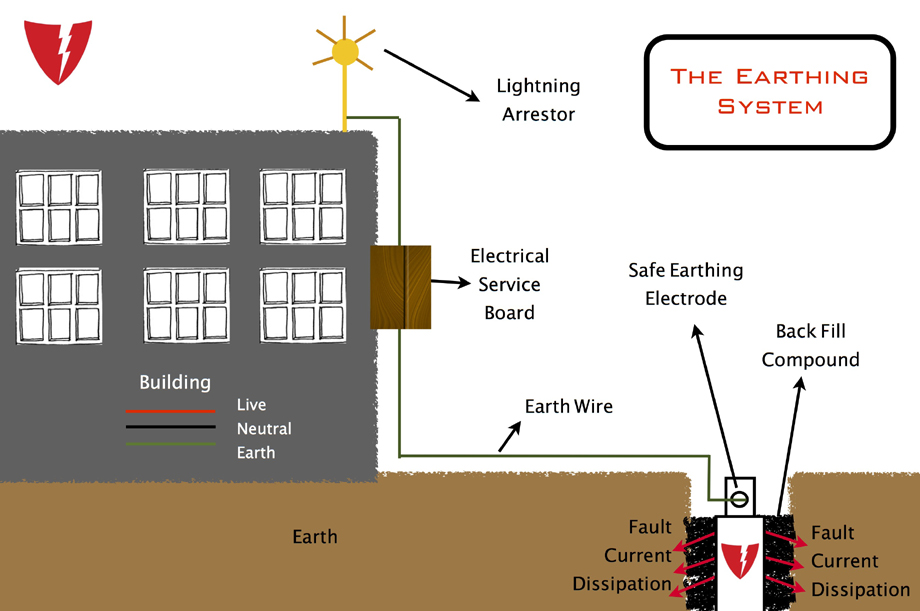
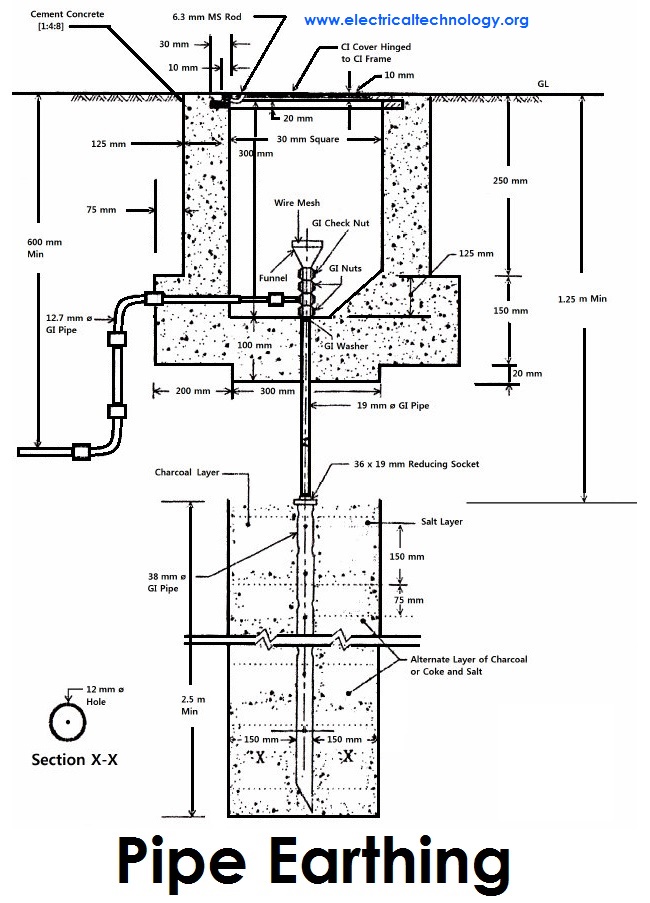
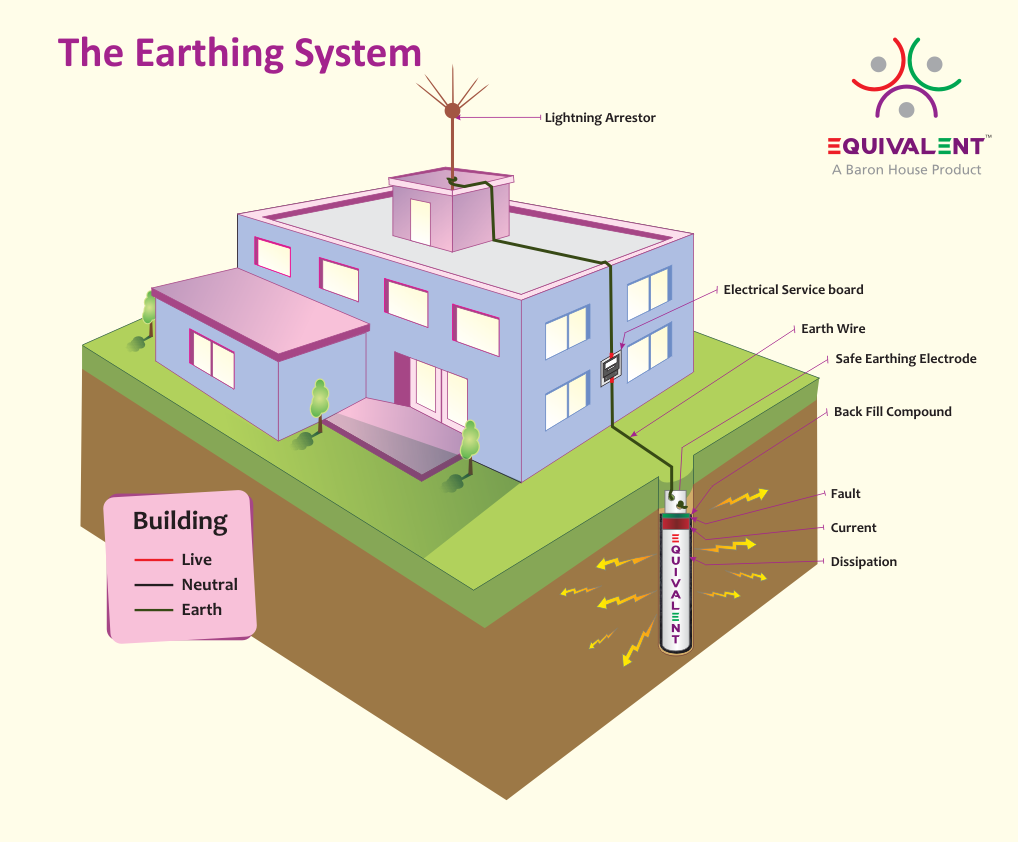
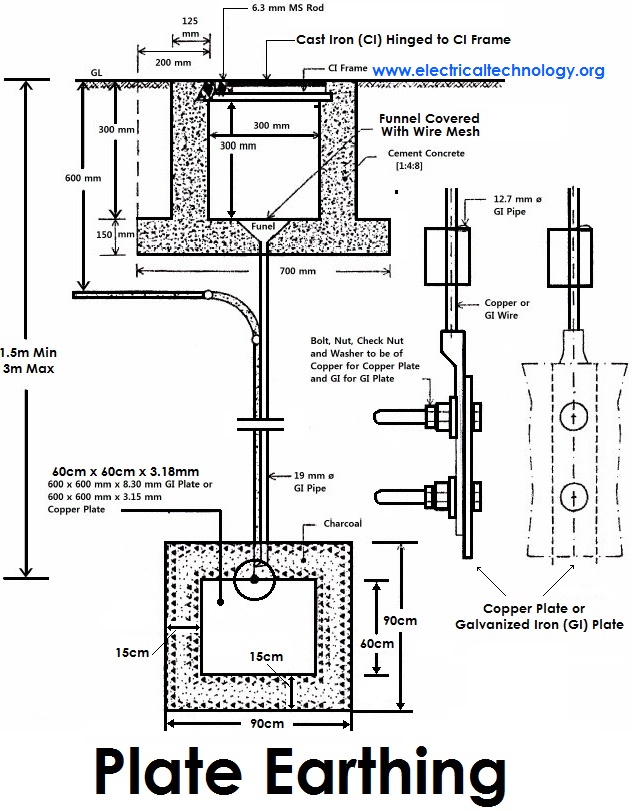
- a connection between an electrical circuit or device and the earth, which is at zero potential
- a terminal to which this connection is madeUS and Canadian equivalent: ground
- Also called: earth colour any of various brown pigments composed chiefly of iron oxides
- (modifier) astrology of or relating to a group of three signs of the zodiac, Taurus, Virgo, and CapricornCompare air (def. 20), fire (def. 24), water (def. 12)
- cost the earth informal to be very expensive
- come back to earth or come down to earth to return to reality from a fantasy or daydream
- on earth used as an intensifier in such phrases as what on earth, who on earth, etc
- run to earth
- to hunt (an animal, esp a fox) to its earth and trap it there
- to find (someone) after searching
verb
- (intr) (of a hunted fox) to go to ground
- (tr) to connect (a circuit, device, etc) to earth
Old English eorþe “ground, soil, dry land,” also used (along with middangeard) for “the (material) world” (as opposed to the heavens or the underworld), from Proto-Germanic *ertho (cf. Old Frisian erthe “earth,” Old Saxon ertha, Old Norse jörð, Middle Dutch eerde, Dutch aarde, Old High German erda, German Erde, Gothic airþa), from PIE root *er- (2) “earth, ground” (cf. Middle Irish -ert “earth”). The earth considered as a planet was so called from c.1400.
n.
- Any of several metallic oxides, such as alumina or zirconia, from which it is difficult to remove oxygen. No longer in technical use.
- The third planet from the Sun and the densest planet in the solar system. Earth is a terrestrial or inner planet consisting of a thin outer crust, an intermediate mantle, and a dense inner core. It has an atmosphere composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen and is the only planet on which water in liquid form exists, covering more than 70 percent of its surface. It is also the only planet on which life is known to have evolved, occupying the relatively thin region of water, land, and air known as the biosphere. Earth has a single, relatively large natural satellite, the Moon. See more at atmosphere core crust mantle. See Table at solar system.
- earth
- Electricity See ground.
The planet on which we live — the third planet from the sun.
see down to earth; ends of the earth; four corners of the earth; move heaven and earth; not have an earthly chance; on earth; run to earth; salt of the earth.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary