noun Physics.
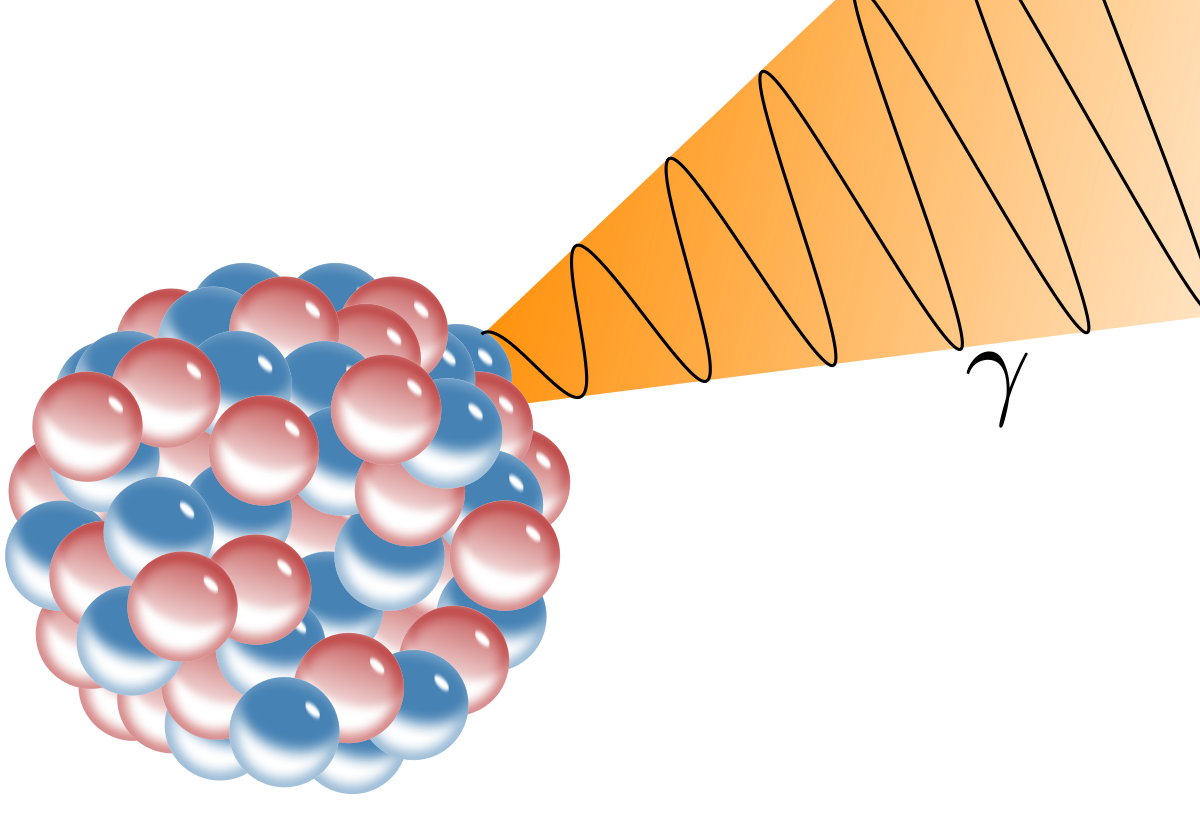
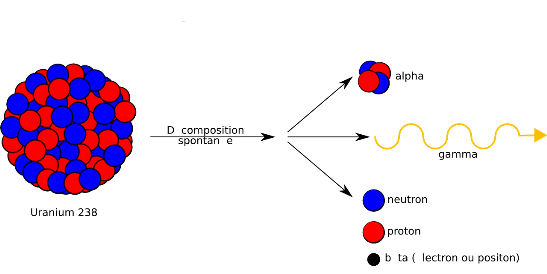
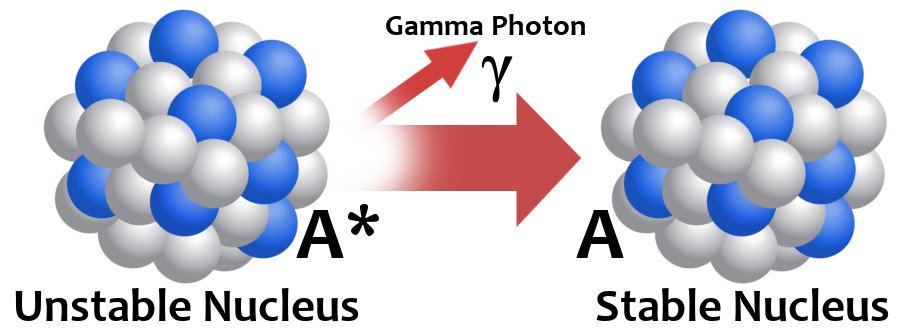
- a photon of penetrating electromagnetic radiation (gamma radiation) emitted from an atomic nucleus.
- a photon emitted by an electron as a result of internal conversion.
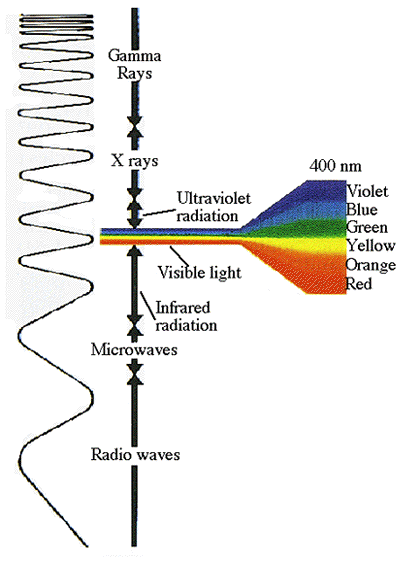
- electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than approximately one tenth of a nanometer.
noun
- electromagnetic radiation emitted by atomic nuclei; the wavelength is generally in the range 1 × 10 –10 to 2 × 10 –13 metres
- electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength emitted by any source, esp the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with a wavelength less than about 1 × 10 –11 metres
n.
- Electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus of an atom by radioactive decay and having energies in a range from ten thousand (104) to ten million (107) electron volts.
- A stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. Because the wavelengths of gamma rays are shorter than those of x-rays, gamma rays have greater energy and penetrating power than x-rays. Gamma rays are emitted by pulsars, quasars, and radio galaxies but cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere. See more at radioactive decay.
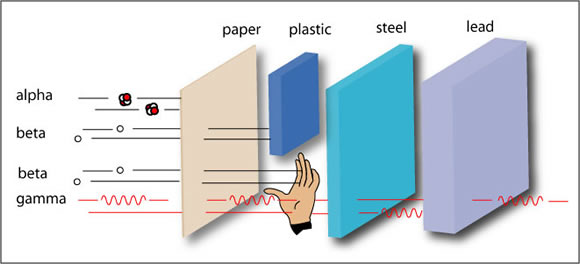
The most energetic radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum; it has the lowest wavelength and the highest frequency in the spectrum. Gamma rays are sent out by some radioactive nuclei. Unlike alpha radiation and beta radiation, gamma rays are not made up of particles, and they have no charge.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary