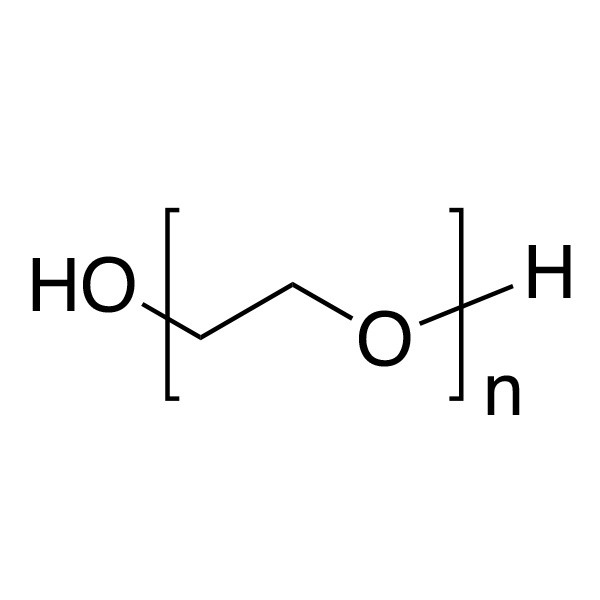
glycol [glahy-kawl, -kol] ExamplesWord Origin noun
- Also called ethylene glycol, ethylene alcohol. a colorless, sweet liquid, C2H6O2, used chiefly as an automobile antifreeze and as a solvent.
- Also called diol. any of a group of alcohols containing two hydroxyl groups.
Origin of glycol First recorded in 1855–60; glyc(erin) + (alcoh)ol Examples from the Web for glycol Historical Examples of glycol
On boiling with water, it decomposes into glycol and trimethylamine.
Poisons: Their Effects and Detection
Alexander Wynter Blyth
No glycollic acid, oxalic acid, glycol, or glycerol was produced.
Arthur Harden
Glycol, glī′kol, n. the type of a class of artificial compounds forming chemically a link between alcohol and glycerine.
Chambers’s Twentieth Century Dictionary (part 2 of 4: E-M)
Various
Glycol is heated in a distillery apparatus to 148 C., and a slow current of dry hydrochloric acid passed through it.
Scientific American, September 29, 1883 Supplement. No. 404
Various
British Dictionary definitions for glycol glycol noun
- another name (not in technical usage) for ethanediol, diol
Derived Formsglycolic or glycollic (ɡlaɪˈkɒlɪk), adjective glycol in Medicine glycol [glī′kôl′, -kōl′] n.
- Any of various alcohols containing two hydroxyl groups.
- Ethylene glycol.
glycol in Science glycol [glī′kôl′, -kōl′]
- See ethylene glycol.
- Any of various alcohols containing two hydroxyl groups (OH).
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary