homology [huh-mol-uh-jee, hoh-] ExamplesWord Origin noun, plural ho·mol·o·gies.
- the state of being homologous; homologous relation or correspondence.
- Biology.
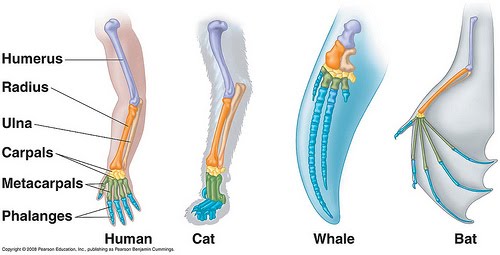
- a fundamental similarity based on common descent.
- a structural similarity of two segments of one animal based on a common developmental origin.
- Chemistry. the similarity of organic compounds of a series in which each member differs from its adjacent compounds by a fixed increment, as by CH2.
- Mathematics. a classification of figures according to certain topological properties.
Origin of homology 1650–60; Greek homología agreement, equivalent to homólog(os) homologous + -ia -y3 Related Words for homologies parity, impartiality, identity, fairness, tolerance, coordination, comparison, metaphor, parallel, correlation, correspondence, par, likeness, evenness, uniformity, equivalence, parallelism, equilibrium, equipoise, sameness Examples from the Web for homologies Historical Examples of homologies
Homologies are not given since these are reviewed by Hudson.
Myology and Serology of the Avian Family Fringillidae
William B. Stallcup
Homologies of parts are best determinable, ceteris paribus, in the most nearly related forms.
A Guide to the Study of Fishes, Volume 1 (of 2)
David Starr Jordan
Homologies more perfect than those connecting man with the great group of monkeys could not exist.
Various
British Dictionary definitions for homologies homology noun plural -gies
- the condition of being homologous
- chem the similarities in chemical behaviour shown by members of a homologous series
- zoology the measurable likenesses between animals, as used in grouping them according to the theory of cladistics
Word Origin for homology C17: from Greek homologia agreement, from homologos agreeing; see homologate homologies in Science homology [hə-mŏl′ə-jē]
- A homologous relationship or correspondence.
- The relation of the chemical elements of a periodic family or group.
- The relation of the organic compounds forming a homologous series.
- A topological classification of configurations into distinct types that imposes an algebraic structure or hierarchy on families of geometric figures.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary