- See under glucose(def 1).
noun Biochemistry.
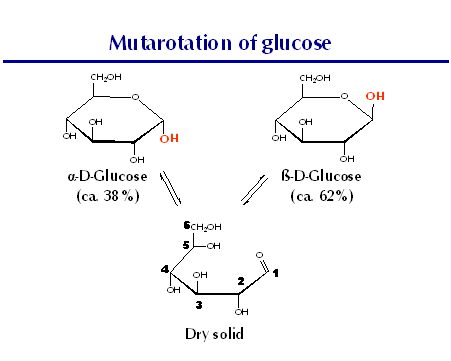
- a sugar, C6H12O6, having several optically different forms, the common dextrorotatory form (dextroglucose, or -glucose) occurring in many fruits, animal tissues and fluids, etc., and having a sweetness about one half that of ordinary sugar, and the rare levorotatory form (levoglucose, or -glucose) not naturally occurring.
- Also called starch syrup. a syrup containing dextrose, maltose, and dextrine, obtained by the incomplete hydrolysis of starch.
noun
- a white crystalline monosaccharide sugar that has several optically active forms, the most abundant being dextrose: a major energy source in metabolism. Formula: C 6 H 12 O 6
- a yellowish syrup (or, after desiccation, a solid) containing dextrose, maltose, and dextrin, obtained by incomplete hydrolysis of starch: used in confectionery, fermentation, etc
n.1840, from French glucose (1838), said to have been coined by French professor Eugène Melchior Péligot (1811-1890) from Greek gleukos “must, sweet wine,” related to glykys “sweet, delightful, dear,” from *glku-, dissimilated in Greek from PIE *dlk-u- “sweet” (cf. Latin dulcis). It first was obtained from grape sugar. n.
- A monosaccharide sugar in the blood that serves as the major energy source of the body; it occurs in most plant and animal tissue.blood sugar
- A monosaccharide sugar found in plant and animal tissues. Glucose is a product of photosynthesis, mostly incorporated into the disaccharide sugar sucrose rather than circulating free in the plant. Glucose is essential for energy production in animal cells. It is transported by blood and lymph to all the cells of the body, where it is metabolized to form carbon dioxide and water along with ATP, the main source of chemical energy for cellular processes. Glucose molecules can also be linked into chains to form the polysaccharides cellulose, glycogen, and starch. Chemical formula: C6H12O6. See more at cellular respiration Krebs cycle photosynthesis.
The most common form of sugar, found extensively in the bodies of living things; a molecule composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen.
[ad_2]
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary