lipid [lip-id, lahy-pid] Word Origin noun Biochemistry.
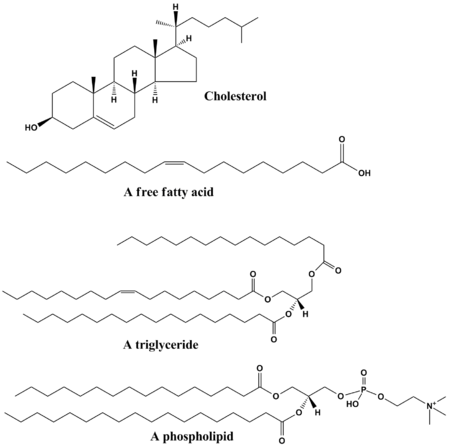
- any of a group of organic compounds that are greasy to the touch, insoluble in water, and soluble in alcohol and ether: lipids comprise the fats and other esters with analogous properties and constitute, with proteins and carbohydrates, the chief structural components of living cells.
Also lip·ide [lip-ahyd, -id, lahy-pahyd, -pid] /ˈlɪp aɪd, -ɪd, ˈlaɪ paɪd, -pɪd/. Origin of lipid First recorded in 1920–25; lip- + -id3 British Dictionary definitions for lipid lipid lipide noun
- biochem any of a large group of organic compounds that are esters of fatty acids (simple lipids, such as fats and waxes) or closely related substances (compound lipids, such as phospholipids): usually insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and other organic solvents. They are important structural materials in living organismsFormer name: lipoid
Word Origin for lipid C20: from French lipide, from Greek lipos fat Word Origin and History for lipid n.
“organic substance of the fat group,” from French lipide, coined 1923 by G. Bertrand from Greek lipos “fat, grease” (see lipo-) + chemical suffix -ide.
lipid in Medicine lipid [lĭp′ĭd, lī′pĭd] n.
- Any of a group of organic compounds, including the fats, oils, waxes, sterols, and triglycerides, that are insoluble in water but soluble in common organic solvents, are oily to the touch, and together with carbohydrates and proteins constitute the principal structural material of living cells.
Related formslip•id′ic adj. lipid in Science lipid [lĭp′ĭd]
- Any of a large group of organic compounds that are oily to the touch and insoluble in water. Lipids include fatty acids, oils, waxes, sterols, and triglycerides. They are a source of stored energy and are a component of cell membranes.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary