noun
- Biology, Physiology. the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which its material substance is produced, maintained, and destroyed, and by which energy is made available.Compare anabolism, catabolism.
- any basic process of organic functioning or operating: changes in the country’s economic metabolism.
noun
- the sum total of the chemical processes that occur in living organisms, resulting in growth, production of energy, elimination of waste material, etcSee anabolism, basal metabolism, catabolism
- the sum total of the chemical processes affecting a particular substance in the bodycarbohydrate metabolism; iodine metabolism
n.in physiology sense, 1878, from French métabolisme, from Greek metabole “a change,” from metaballein “to change,” from meta- “over” (see meta-) + ballein “to throw” (see ballistics). n.
- The complex of physical and chemical processes occurring within a living cell or organism that are necessary for the maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized.
- The functioning of a specific substance, such as water, within the living body.
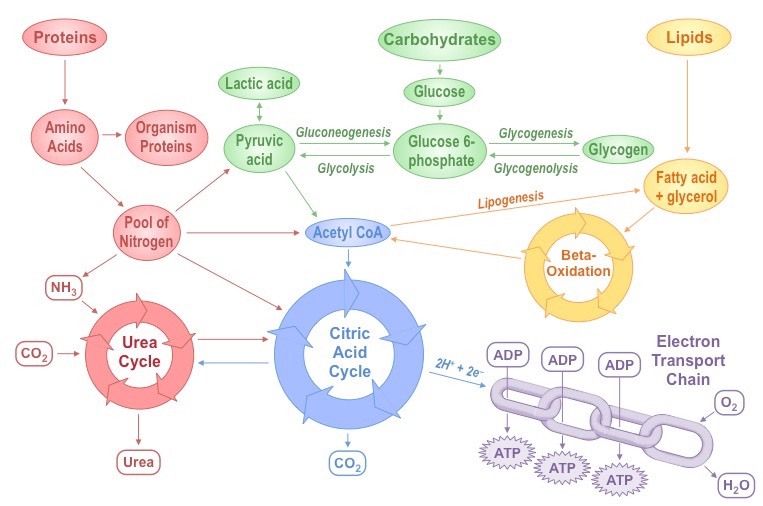
- The chemical processes by which cells produce the substances and energy needed to sustain life. As part of metabolism, organic compounds are broken down to provide heat and energy in the process called catabolism. Simpler molecules are also used to build more complex compounds like proteins for growth and repair of tissues as part of anabolism. Many metabolic processes are brought about by the action of enzymes. The overall speed at which an organism carries out its metabolic processes is termed its metabolic rate (or, when the organism is at rest, its basal metabolic rate). Birds, for example, have a high metabolic rate, since they are warm-blooded, and their usual method of locomotion, flight, requires large amounts of energy. Accordingly, birds usually need large amounts of high-quality, energy-rich foods such as seeds or meat, which they must eat frequently. See more at cellular respiration.
The total of the chemical reactions that maintain the life of a living thing.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary