noun Pathology.
- the presence of an abnormally large number of mononuclear leukocytes, or monocytes, in the blood.
- infectious mononucleosis.
noun
- pathol the presence of a large number of monocytes in the blood
- See infectious mononucleosis
n.1920, coined from mononuclear + Modern Latin -osis “abnormal condition.” n.
- Abnormally large numbers of mononuclear white blood cells in the blood, especially forms that are not normal.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
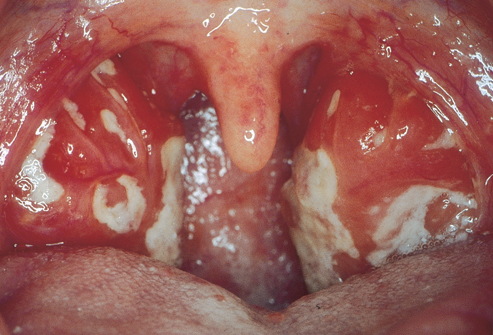
- A common infectious disease usually affecting young people, caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and characterized by fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue. The symptoms may last for several weeks.
An acute and infectious disease caused by a virus; its symptoms include fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, and general exhaustion. Mononucleosis gets its name from the kind of white blood cell (monocyte) that increases in number in the blood of persons who have the disease. There is no specific treatment, but sufferers usually recover within a few weeks.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary