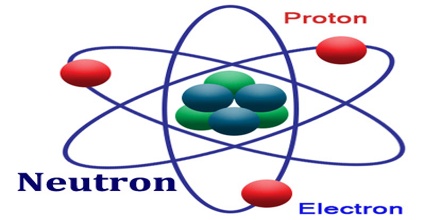
noun Physics.
- an elementary particle having no charge, mass slightly greater than that of a proton, and spin of ½: a constituent of the nuclei of all atoms except those of hydrogen. Symbol: n
noun
- physics a neutral elementary particle with a rest mass of 1.674 92716 × 10 –27 kilogram and spin 1/2; classified as a baryon. In the nucleus of an atom it is stable, but when free it decays
n.“electrically neuter particle of the atom,” 1921, coined by U.S. chemist William D. Harkins (1873-1951) from neutral (adj.) + -on. First record of neutron bomb is from 1960. Neutron star attested from 1934, originally hypothetical; so called because it would be composed of neutrons. n.
- An electrically neutral subatomic particle in the baryon family, having a mass 1,839 times that of the electron, stable when bound in an atomic nucleus, and having a mean lifetime of approximately 1.0X103 seconds as a free particle. It and the proton form nearly the entire mass of atomic nuclei.
- An electrically neutral subatomic particle in the baryon family, having a mass of 1.674 X 10-24 grams (1,838 times that of the electron and slightly greater than that of the proton). Neutrons are part of the nucleus of all atoms, except hydrogen, and have a mean lifetime of approximately 1.0X103 seconds as free particles. They consist of a triplet of quarks, including two down quarks and one up quark, bound together by gluons. In radioactive atoms, excess neutrons are converted to protons by beta decay. Beams of neutrons from nuclear reactors are used to bombard the atoms of various elements to produce fission and other nuclear reactions and to determine the atomic arrangements in molecules. See Table at subatomic particle.
An elementary particle without an electrical charge; one of the building blocks of the nucleus of the atom. A neutron has about the same mass as a proton.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary