noun Pathology.
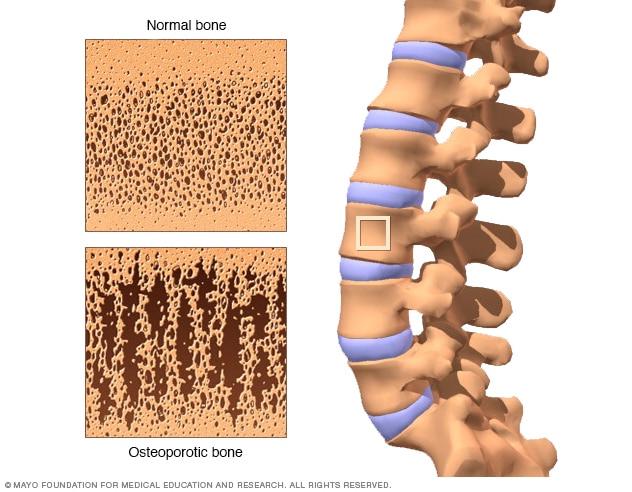
- a disorder in which the bones become increasingly porous, brittle, and subject to fracture, owing to loss of calcium and other mineral components, sometimes resulting in pain, decreased height, and skeletal deformities: common in older persons, primarily postmenopausal women, but also associated with long-term steroid therapy and certain endocrine disorders.
noun
- porosity and brittleness of the bones due to loss of calcium from the bone matrix
n.1846, from osteo- + stem of Greek poros “passage, pore, voyage” (see pore (n.)) + -osis. Related: Osteoporotic. n. pl. os•te•o•po•ro•ses (-sēz)
- A disease characterized by decrease in bone mass and density, occurring especially in postmenopausal women, resulting in a predisposition to fractures and bone deformities such as vertebral collapse.
- A bone disease characterized by decrease in bone mass and density, resulting in a predisposition to fractures and bone deformities such as the collapse of one or more vertebrae. It occurs most commonly in women after menopause as a result of estrogen deficiency. Calcium supplementation and weight-bearing exercise are used to treat and prevent osteoporosis.
A softening of the bones that gradually increases and makes them more fragile. It is caused by the gradual loss of the mineral calcium, which helps make bones hard. Osteoporosis occurs most often in elderly women.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary