noun Anatomy, Zoology.
- a gland, situated near the stomach, that secretes a digestive fluid into the intestine through one or more ducts and also secretes the hormone insulin.
noun
- a large elongated glandular organ, situated behind the stomach, that secretes insulin and pancreatic juice
n.1570s, from Latinized form of Greek pankreas “sweetbread (pancreas as food), pancreas,” literally “entirely flesh,” from pan- “all” (see pan-) + kreas “flesh” (see raw), probably on notion of homogeneous substance of the organ. n. pl. pan•cre•a•ta (păng-krē′ə-tə)
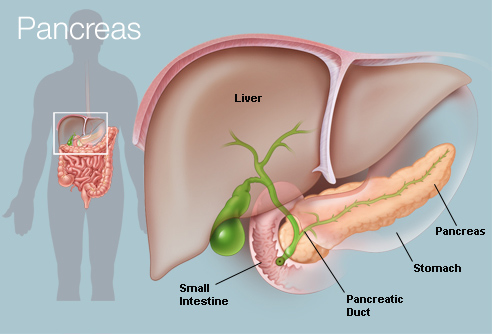
- A lobulated gland without a capsule, extending from the concavity of the duodenum to the spleen, consisting of a flattened head within the duodenal concavity, an elongated three-sided body extending across the abdomen, and a tail touching the spleen, and secreting insulin and glucagon internally and pancreatic juice externally into the intestine.
- A long, irregularly shaped gland in vertebrate animals that is located behind the stomach and is part of the digestive system. It secretes hormones (insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin) into the bloodstream and digestive enzymes into the small intestine or gut. The pancreas also secretes sodium bicarbonate, which protects the lining of the intestine by neutralizing acids from the stomach.
A gland behind the stomach that functions in both the endocrine system and the digestive system. Its endocrine function involves the secretion into the bloodstream of insulin, which regulates the level of sugars in the blood. As part of the digestive system, the pancreas secretes into the small intestine a fluid containing enzymes that is used in the digestion of all foods.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary