noun, plural throm·bi [throm-bahy] /ˈθrɒm baɪ/. Pathology.
- a fibrinous clot that forms in and obstructs a blood vessel, or that forms in one of the chambers of the heart.
noun plural -bi (-baɪ)
- a clot of coagulated blood that forms within a blood vessel or inside the heart and remains at the site of its formation, often impeding the flow of bloodCompare embolus
n.1690s, Modern Latin, from Greek thrombos “lump, piece, clot of blood, curd of milk.” n. pl. throm•bi (-bī)
- A fibrinous clot formed in a blood vessel or in a chamber of the heart.
Plural thrombi (thrŏm′bī′)
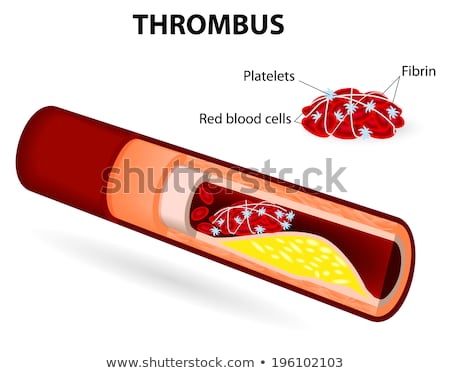
- A clot consisting of fibrin, platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells that forms in a blood vessel or in a chamber of the heart and can obstruct blood flow. The rupture of atherosclerotic plaques can cause arterial thrombosis (the formation of thrombi), while tissue injury, decreased movement, oral contraceptives, prosthetic heart valves, and various metabolic disorders increase the risk for venous thrombosis. A thrombus in a coronary artery can cause a heart attack. Compare embolus.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary