noun, plural tra·che·ae [trey-kee-ee or, esp. British, truh–kee-ee] /ˈtreɪ kiˌi or, esp. British, trəˈki i/, tra·che·as.
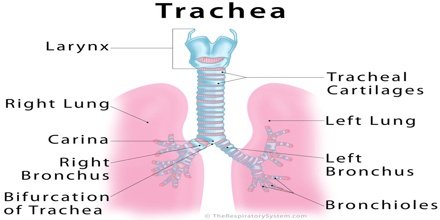
- Anatomy, Zoology. the tube in humans and other air-breathing vertebrates extending from the larynx to the bronchi, serving as the principal passage for conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
- (in insects and other arthropods) one of the air-conveying tubes of the respiratory system.
- Botany. vessel(def 5).
noun plural -cheae (-ˈkiːiː)
- anatomy zoology the membranous tube with cartilaginous rings that conveys inhaled air from the larynx to the bronchiNontechnical name: windpipe
- any of the tubes in insects and related animals that convey air from the spiracles to the tissues
- botany another name for vessel (def. 5), tracheid
c.1400, from Medieval Latin trachea (mid-13c.), as in trachea arteria, from Late Latin trachia (c.400), from Greek trakheia, in trakheia arteria “windpipe,” literally “rough artery” (so called from the rings of cartilage that form the trachea), from fem. of trakhys “rough.” See artery for connection with windpipe in Greek science.
n. pl. tra•che•as
- The airway that extends from the larynx into the thorax where it divides into the right and left bronchi. It is composed of thin incomplete rings of hyaline cartilage connected by a membrane called the annular ligament.windpipe
Plural tracheae (trā′kē-ē′) tracheas
- The tube in vertebrate animals that leads from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and carries air to the lungs. In mammals the trachea is strengthened by rings of cartilage. Also called windpipe
- Any of the tiny tubes originating from the spiracles of many terrestrial arthropods and forming a branching network that brings air directly to body cells.
The tube connecting the mouth to the bronchial tubes that carries air to the lungs; the windpipe.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary