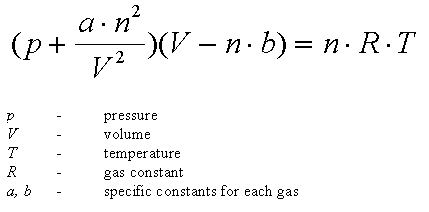
noun Thermodynamics.
- an equation of state relating the pressure, volume, and absolute temperature of a gas, taking into account the finite size of the molecules and the attractive force between them.
noun
- an equation of state for a non-ideal gas that takes account of intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the molecules of the gas
- An equation that relates the pressure, volume, and absolute temperature of a gas taking into account the finite size of molecules, and their intermolecular attraction, having the form RT = (P + av-2)(v – b), where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, P is the pressure, v is the volume of fluid per molecule, a is a measure of the attraction of the molecules for each other (due to van der Waals forces), and b is the volume occupied by a single molecule. The equation accurately captures phase transitions between liquid and gas phases of substances. See also ideal gas law.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary