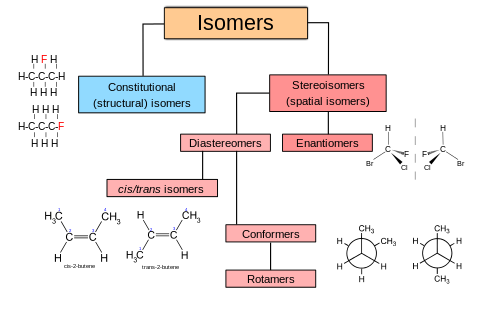
isomer [ahy-suh-mer] ExamplesWord Origin noun
- Chemistry. a compound displaying isomerism with one or more other compounds.
- Also called nuclear isomer. Physics. a nuclide that exhibits isomerism with one or more other nuclides.
Origin of isomer First recorded in 1865–70; back formation from isomeric Examples from the Web for isomer Historical Examples of isomer
Sometimes either form was digestible, but frequently the body could use only the isomer to which it was adjusted.
Lester del Rey
According to this view hyoscyamine ought to be the hyoscinate of hyoscine, or at any rate an isomer of this body.
Scientific American Supplement, No. 324, March 18, 1882
Various
An isomer of chloral, parachloralide, is made by passing excess of dry chlorine into absolute methyl alcohol.
Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 3
Various
Besides this oil, cloves also contain two neutral bodies, eugenin and caryophyllin, the latter of which is an isomer of camphor.
Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 5
Various
Chavibetol, an isomer of eugenol, occurs in the ethereal oil obtained from Piper betle.
Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 9, Slice 8
Various
British Dictionary definitions for isomer isomer noun
- chem a compound that exhibits isomerism with one or more other compounds
- physics a nuclide that exhibits isomerism with one or more other nuclides
Derived Formsisomeric (ˌaɪsəˈmɛrɪk), adjective Word Origin and History for isomer n.
1866, back-formation from isomeric; cf. Greek isomeres “sharing equality,” from iso- (see iso-) + meros “part, share” (see merit (n.)).
isomer in Medicine isomer [ī′sə-mər] n.
- Any of two or more substances that are composed of the same elements in the same proportions but differ in properties because of differences in the arrangement of atoms.
- Any of two or more nuclei with the same mass number and atomic number that have different radioactive properties and can exist in any of several energy states for a measurable period of time.
Related formsi′so•mer′ic (-mĕr′ĭk) adj. isomer in Science isomer [ī′sə-mər]
- Chemistry Any of two or more substances that have the same molecular formula but differ in their connectivity or spatial arrangement of atoms, or in their topology in macromolecules.
- Physics Any of two or more nuclei with the same mass number and atomic number that have different radioactive properties and can exist in any of several energy states for a measurable period of time.
 Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary
Liberal Dictionary English Dictionary